proj0&1
Note1 Basic Queries
NULL的处理
- NULL的任何计算都是NULL,包括x = NULL
- WHERE NULL 意味着 WHERE FALSE,不会包含任何结果
聚合
- 除COUNT(*)之外,每个聚合函数都忽略NULL值,因此COUNT(
) 返回指定列的非NULL值数量,而COUNT(*)返回整个表中的行数
HAVING
- WHERE occurs before grouping. It filters out uninteresting rows. WHERE 发生在分组之前。它过滤掉不感兴趣的行。
- HAVING occurs after grouping. It filters out uninteresting groups. HAVING 发生在分组之后。它过滤掉不感兴趣的群体。
Note2 Joins & Subqueries
- Subquery Factoring
- WITH 提取一个子查询
-- 用名称简化
WITH courseEnrollment AS (
SELECT c.num AS num1, c.name, e.num AS num2, e.students
FROM courses AS c INNER JOIN enrollment AS e
ON c.num = e.num;
)
-- 将简化的courseEnrollment当成自己的表
SELECT num1, name, students
FROM courseEnrollment
WHERE students > 700;
Note3 Disks and Files
Memory and Disk
-
磁盘的读写效率很低,传输的单位是页
-
访问磁盘(读写)页面/块 的时间:
-
seek time (moving arms to position disk head on track); 2-3 ms on average
寻道时间(移动磁臂将磁盘头定位在磁道上); 平均 2-3 毫秒
-
rotational delay (waiting for block to rotate under head); 0-4 ms (15000 RPM)
旋转延迟(等待方块在头下旋转); 0-4 毫秒(15000 转/分钟)
-
transfer time (actually moving data to/from disk surface); 0.25 ms per 64KB page
传输时间(实际将数据移入/移出磁盘表面);每 64KB 页 0.25 毫秒
-
-
磁盘空间管理
- 磁盘空间管理是 DBMS 的最低层。它负责管理磁盘空间。其主要用途包括将页面映射到磁盘上的位置、将页面从磁盘加载到内存以及将页面保存回磁盘并确保写入。
Files, Pages, Records
-
关系型数据库系统的基本单位是record (row),record被组织成relations (tables) ,可以在内存中被增删改查。
-
磁盘数据的基本单位是page,每张表被被组织成多个page形成了一个file,file被组织成database。
-
Based on the relation’s schema and access pattern, the database will determine: (1) type of file used, (2) how pages are organized in the file, (3) how records are organized on each page, (4) and how each record is formatted.
基于关系模式的访问模式,数据库将决定:(1) 使用的文件类型,(2) 文件中的页面如何组织,(3) 每个页面上的记录如何组织,(4) 以及每个页面如何组织记录已格式化。
Choosing File Types
- There are two main types of files: Heap Files and Sorted Files.
- 对于每张表,数据库将�通过I/O成本来选择类型,1I/O相当于读或者写一页
Heap File
- 一种文件类型,没有特定的页面顺序
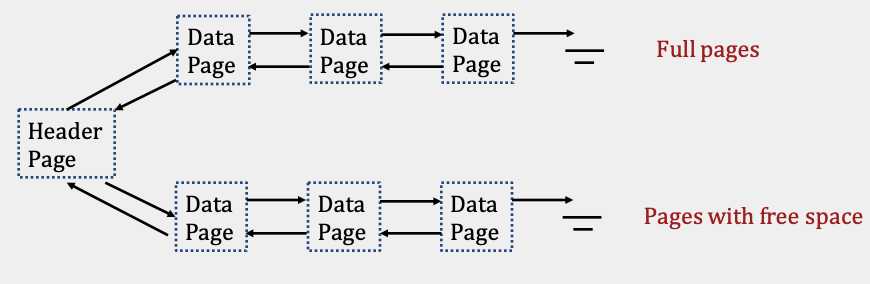
链表实现
- 每个数据页包含了records(很多行), free space tracker,上下页指针
- 数据页分为完整页和空闲页,full pages and free page。
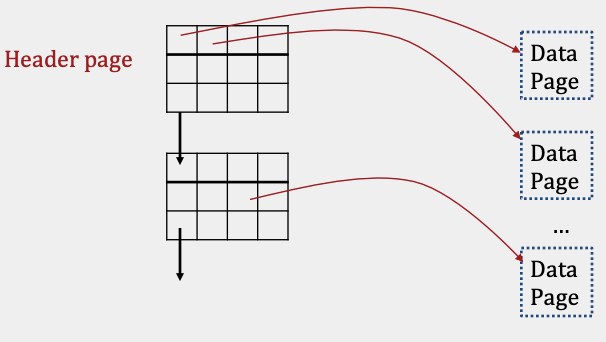
- 有一个 header page
Page Directory Implementation 页目录实现
- 和链表实现的不同在于:using a linked list for header pages,在标头页使用链表
- 标头页包含指针和可用空间
- 数据页仅存数据
相对链表的优点是插入快 搜索相对都比较慢,需要完整扫描
Sorted Files
- 页是按照key有序排序的
- 没说实现,但是查找用二分,复杂度:logN I/Os
- 插入可能会移动后面的页, logN + N I/O
A Note on Counting Header Pages
- 关于需不需要计算Header的IO成本
Record Types
行的格式
- 固定长度记录(FLR)和可变长度记录(VLR)
- VLR的时候,Header要记录Record的尾部
Page Formats
页的格式
- Pages with Fixed Length Records
- 用page headers去存储当前的records数量
- 因为知道了record的数量和长度,所以插入很容易
- Pages with Variable Length Records
- 有一个page footer去维护 a slot directory 用来跟踪 slot count, a free space pointer, and entries
Field Types
cs186的约定
| Type | Data Type | Size (B) |
|---|---|---|
| Fixed | Integer | 4 |
| Fixed | Float | 4 |
| Fixed | Boolean | 1 |
| Fixed | Byte | 1 |
| Fixed | Char(N) | N |
| Variable | Varchar(N) | <= N |
| Variable | Text | >= 0 |
总结和问题
- 每个文件包含了多页,每页里面有多行
- 是不是一个文件对应一张表
- 对于索引来说,索引是file之上的东西,还是说index file也是一种file,和sorted file是同级的概念
- 什么是页的packed和unpacked